Sump pumps remove water which accumulates in the low points in a building,
typically the basement. They are an effective and affordable way to reduce
costly flood damages.
Description + function
Sumps are typically built in sump basins in basement floors but can also be incorporated into slab-on-grade floors and elevator pits. Pumps are installed in these sump basins to remove water during minor to moderate floods.
Sump pumps are designed for intermittent use. Chronic water problems require repairing the drainage system.
Strategy into action
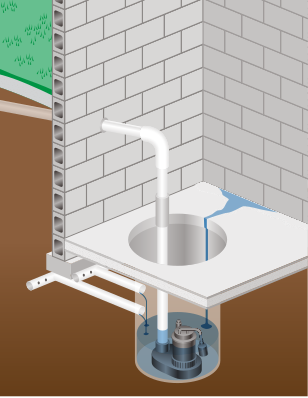
Sump pumps should be installed at low points in a basement floor to collect water, reducing water damage risk to vital equipment. If a concrete floor is uneven and water collects in puddles, channels can be cut into the slab, allowing the water to drain.
A basement sump can be a source of radon, a radioactive gas naturally occurring in some soils. If radon levels are too high or if required by code, a heavy-duty cover with an outside vent pipe may be installed.
Float switch-activated submersible sump pumps are recommended for permanent locations; they will start pumping water automatically once water reaches a certain level.
A sump pump rated at 5.5 amps can remove about 100 gallons of water a minute. A lower vertical rise or a larger pump will remove more water more quickly. Determine the number and size of the sump pumps you need based on:
- Maximum amount of water anticipated in a flood.
- How high water needs to be pumped.

Design sump pumps to handle moderate flooding but not catastrophic flooding such as a coastal storm surge.
Power supplies for sump pumps should be rated for submersion, and wiring should extend up from this equipment rather than along the floor. Locate controls for the system above the DFE. Pumps should be connected to an emergency backup generator to maintain power during outages. Be sure that the generator has adequate capacity to power the pumps. Some sump pumps require considerable power draw so battery power may not be adequate.
Operations + maintenance
Inspect regularly.
Inspect permanently installed sump pumps regularly to ensure that they are in good working condition.
Check and clean the pump inlet screen, particularly while in operation, since debris or blockage can drastically reduce flow rates.
Estimated cost
-
$
-
$$
-
$$$
-
$$$$
Supporting strategies
Resources
- Sizing up a Sump Pump, Land and Water, Conserving Natural Resources in Illinois. abe-research.illinois.edu/pubs/factsheets/SumpPumps.pdf
- Sump Pumps, Dry Floodproofing Measures, Section 3.7.1, pages 3-27, FEMA Guidance for non-residential buildings, July 2013. www.fema.gov/media-library/assets/documents/34270
Background
Operated by the Fifth Avenue Committee, the three-story, four-unit property at 190 Butler Street in Brooklyn was built in 1920. It is on the border of the 100-year AE FEMA flood zone.
Sewer system backflow from Superstorm Sandy drove water into the cellar to a height of about 10 inches above the floor. Electrical circuits, junction boxes and light fixtures were damaged, though fortunately only in a small area of the cellar.
Strategy
FAC hired a plumber to install a sump pump at the lowest point in the basement. It has a floater device that controls the power. When water rises to a certain level, the floating valve activates the pump. When the water level in the sump drops sufficiently, the pump shuts off automatically.
Cost
$2,000, not including installation.


